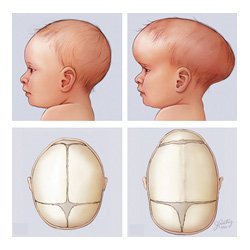
Craniosynostosis is a congenital defect that causes premature closure (fusion) of one or more of the soft joints within the bones of a child’s skull before the child’s brain is fully developed. As the brain continues to grow, this results in a distorted appearance with increased brain pressure.
Treatment for craniosynostosis involves surgery to correct the shape of the head and allow the brain to grow normally.
Early diagnosis and treatment allows enough room for a child’s brain to develop.
symptoms craniosynostosis
1. A distorted skull
2. An abnormal sensation or a lump that is hidden in the baby’s skull
3. Development of a solid raised bump through the affected cranial sutures
4. Slow or no head growth during a child’s development
Types
Nomocephaly
Trigonocephaly
Brachycephaly
Scaphocephaly
Posterior plagiocepgaly
Anterior plagiocepgaly
Complications
May cause permanent deformity of the face and head
Risk of increased intracranial pressure leading to:
1. growth retardation
2. Cognitive weakness
3. lack of energy
4. blindness
5. Eye movement disorders
6. epileptic seizures
7. Death
before the Craniosynostosis operation
1. Plastic surgeon (specialty in craniofacial surgery)
2. Pediatric Neurosurgeon
3. Ear, Nose and Throat surgeon (specialty in airway)
4. Eye surgeon (to check fundus and blood pressure)
5. pediatrician
6. Geneticist and genetics doctor
Types of Craniosynostosis surgeries
1. Closed (hinge) suture excision:
These operations work in some cases at a very early age,
These operations depend on the ability of the head bones to form after the operation, and therefore their results are not guaranteed and unpredictable.
2. skull reshaping:
These operations are performed in cooperation between a craniofacial surgeon (plastic surgeon) and a pediatric neurosurgeon.
It includes reshaping the bones of the skull and eye socket, if necessary, and using screws and plates during the period of fusion of the remodeled bone. These screws and plates dissolve within two years as the body gradually absorbs them.
Usually, the blood is transfused to the child during the operation and then placed in the pediatric intensive care unit for one night. The CT scan is repeated the next morning.
3. Skull distraction procedure:
These operations are performed in cases that are older or in cases of complete closure of the sutures. It involves placing an extension device inside the child’s head with an external part. The father of the child uses a medical screwdriver to rotate the device 3 times daily until the bone is lengthened properly. These operations include a second operation to remove the device.
After the Craniosynostosis operation
1. The child remains in the intensive care unit for one night. The child is then taken to the ward, where he receives intravenous antibiotics and treatments.
2. There is a tube to drain fluids, which is removed after a few days.
When to contact my surgeon after surgery
1. wound redness
2. Severe headache
3. pus
4. change of sight
5. The child was hit on the head
6. The worst is clouding the consciousness of the child
wound care
1. Bathing and exposing the wound to water and unscented baby shampoo is okay without rubbing.
2. Make sure that the child does not get hit on the head or fall in the first six weeks.
3. Apply anti-inflammatory creams as instructed by the medical officer.
4. Use all treatments as instructed by the medical team.
5. Keep the hair short with the extension device and around the device.
6. Wound care and hygiene is important to prevent infections.

